
HOW TO Design A Website
How to design a website step 1
1. Find a Hosting Company
What Features to Look For in A Hosting Service?
Every hosting service provider does have some highlights among the features they can serve. However, to ensure the best one among them for your website, try to find the following factors among the offered features while going through their hosting plans:
1.1 Scale of Resources
Many still tend to think that an unlimited amount of essential resources may cost a fortune. In actuality, there are many web hosts who are capable of providing such amount at very affordable price points. Even the hosting packages built on shared servers can provide you with unlimited bandwidth, websites, storage or email accounts. So keep in mind to pick a provider who can deliver an apt amount of resources without compromising the client budget.
1.2 Loading Speed
As Google said a few years ago – even a two-second delay can cause your website to lose potential customers. Everyone nowadays has a very short attention span. Especially on the internet, where everything happens at the speed of lightning, the online surfers expect every page to load in a few microseconds.
Hence, the web host of your choice needs to provide instantaneous page load. Many providers mention the exact average loading time on their website. Look for information like that on their official site and other reliable sources.
1.3 Uptime Percentage
Even if your website pages take the least time to load, it is of no value when the interested customers can’t even access the site. In this day and age, the uptime of a website has to be at least 99.94% on average. So any web host who provides any lower uptime percentage than that, is not worth considering.
Some hosts even promise to compensate if the website ever goes down for longer than they promised. Pick a provider who is confident enough in their capabilities and whose uptime history for other clients align with their claims.
1.4 Domain Registration
Most leading web hosts take care of the domain registration process for you. All you have to do is pick the domain name of your choice and check its availability. The provider can include this in their hosting plans which means you don’t have to pay any extra amount, they can offer you the registration at a discounted price or they can straight up charge you a few dollars. The first option works the best of course for site owners on a tight budget, but you may choose the others for transparency as well.
1.5 Email Accounts
A good web host lets you have unlimited or a fixed number of email accounts based on the chosen domain name. Besides, certain security measures also come with the package which ensures no spam can enter your inbox. Some of the providers include the perks of auto-responders which prepare a default reply to particular emails.
1.6 Website Transfer
If this is not your first rodeo, you will need a web host who doesn’t charge extra to transfer your site from the previous provider to the new one. You can find this advantage in the hosting plans of most providers. Moving a site from one host to another is a complex task by itself. Taking on the disadvantage of paying extra for the transfer may just add to the inconvenience.
1.7 Backups Frequency
Depending on the set price point, the hosting plans provide data backups in weekly or daily basis. For the more affordable ones, they may impose a fixed number of backups for a day or a certain number of days to deliver the backups. It can also be automatic or manual. Daily automated backups are the most convenient choice.
1.8 Customer Support
Proactive and knowledgeable customer support is crucial to any hosting service. No matter what kind of website you are running, it will definitely become a victim of some crash or issue at some point. If the support team does not respond to your call for help on time, it will cause huge losses for your business. Also, if the team does respond instantaneously but fails to provide the required solution, it is still as bad. So look for 24/7 customer support and if the support team receives any form of training beforehand.
1.9 Security Measures
The most basic standard security measure for a hosted website is having a free SSL certificate. Along with this mandatory feature, your chosen web host must also offer scanning of network and servers. It should also remove the detected malware and protect the site from cyber-attacks. An ecommerce site must be PCI-compliant to guarantee secure financial transactions.
1.10 Developer-Friendly
If your website requires a developer-friendly environment, find a hosting service that is compatible with the popular programming languages and platform. The common hosting service features of this category include support for multiple versions of PHP up to the latest 7.2, Node.js, Perl, Python, Apache and MySQL. All these can be valuable additions to your website hosting package and the developers on your team will be very grateful to have these at their disposal.
1.11 CMS Support
For ecommerce websites, support for a CMS or content management system is crucial. Although WordPress is leading the CMS competition, you can go for more specialized platforms like Magento, Joomla, Drupal, PrestaShop etc. These platforms streamline many time-consuming functions and enable you to organize the site more efficiently.
1.12 Site Builders
Free website builders will make the whole process of establishing your website a lot easier. While there are standalone website builders like Weebly, many hosting services also provide such builders as part of their hosting packages.
How to design a website step 2
2. Choose your website design builder software
Mobirise is a free software website builder that runs on Microsoft Windows or for Mac.
Mobirise is a free offline app for Windows and Mac to easily create small/medium websites, landing pages, online resumes and portfolios. 4500+ beautiful website blocks, templates and themes help you to start easily.
Mobirise is perfect for non-techies who are not familiar with the intricacies of web design and prefer to work as visually as possible. Also great for pro-coders for fast prototyping and small customers’ projects.
Key differences from traditional website builders: Minimalistic, extremely easy-to-use interface; Mobile/Google-friendly, latest website blocks and techniques “out-the-box”; Free for commercial and non-profit use
To Make use of all the functionality they have a Website Builder Kit that will cost you $149 or converted in South African rand R2513.91
![]() Ultimate Freehand. Web Design 3.0
Ultimate Freehand. Web Design 3.0
Website Builder Software. Mobile-Friendly. No Coding
WordPress, Joomla, HTML5, Windows, Mac OS and Online
Absolute Creativity With No Coding, Simple drag-and-drop website builder software to implement any ideas.
WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal became the most popular Content Management Systems. They replaced the self-written systems, which were imperfect and expensive to write and to maintain and which also had limited functionality. Thanks to WordPress and Joomla, anyone could create a blog or website. And today, more than 20% of sites are built using those systems.
WordPress and Joomla always supported themes and templates, which made it possible to modify the design without changing the content. It was possible to create themes manually or buy ready-made ones. Also, webmasters could use Theme Builder. There is a mass of themes and templates available.
To Make use of all the functionality they have a Website Builder Kit that will cost you $129 or converted in South African rand R1903.93
Best for Previewing Sample Sites

Strikingly Website Builder
PROS
- Easy-to-use site-building tools
- Attractive themes, with responsive designs
- Lets you switch templates without rebuilding your site
- Excellent uptime
- Free tier
CONS
- Fewer template choices and less customization than competing website builders
- Many standard features require a premium account
- Not every plan lets you create multi-page sites
- Doesn’t let you sell digital downloads
Best for Building Free Sites

Wix Website Builder
PROS
- Remarkably intuitive Editor X interface
- Numerous widgets
- Hundreds of templates for specific businesses and other uses
- Good mobile-site-building tools
- Rich web-store features
- Excellent uptime and customer service support
- Many commerce options, including the ability to sell digital downloads
- Free option
CONS
- No built-in statistics
- Doesn’t let you switch templates
Best for E-Commerce

Gator Website Builder
PROS
- Strong uptime
- Well-designed interface
- Attractive, modern site templates
- Lets you easily switch themes
- Royalty-free stock photography
- Lets you sell digital downloads
- Excellent prices
- All tiers accept some form of payment
CONS
- Lacks a free plan
- Few photo-editing options
- Cannot schedule blog posts
- Tiny app store
Best for Marketing and SEO Tools

Godaddy website builder
Available at GoDaddyPROS
- Good-looking sites on desktop and mobile
- Unlimited storage and monthly data transfers
- Great marketing and SEO tools
- More than 100 templates
- Excellent uptime
- Good customer service
- Free tier
CONS
- Limited layout customization and photo editing
- Ecommerce not available with all tiers
- Doesn’t let you switch templates
We At Social Media Guru recommend to start with WordPress as WordPress is an opensource software with free functions. However all website design software has its limited functions and feathers in the free plugins.
To really have your website design optimised and responsive with a good website design, good website speed and SEO you would have to be ready to invest some money to make it worth your while.
How to design a website step 3
3. plan website design structure and layout
3.1 Why Plan a Website Structure?
Well, you wouldn’t build a house without a plan, so why would you want to build your business website without it.
It can help to improve your user experience, your SEO, your internal linking and the simplicity of usage.
You should understand that planning a structure isn’t just about the main website, it’s also about the blog and internal linking.
Let’s dive more into details.
3.2 Why Creating a Simple Simple Structure and Sitemap is Not Enough?
By creating a website structure you’ll save yourself a headache. Because you’ll have the list of the pages and the titles right in front of you when creating pages.
Also, you’ll know your pages descriptions up front. Well, at least you’ll have them planned.
This means that you won’t have:
Missing page descriptions
Duplicate titles
Duplicate page descriptions
The fact is, that by doing your research and your website structure before designing a website you’ll know where and what your potential clients are searching for and how you’ll compare to your competitors.
So you see, just a simple sitemap and a structure are not enough.
They are not showing you the right picture if no research is there to back it up.
With the research done you know exactly what pages to create, what the website structure will look like and what content you’ll need. Planning ahead for content marketing.
3.3 Start by Getting the Basic Insights to Your Business
What does this mean?
This means getting to know your own business.
It’s not just important when you talk to a designer or whoever will create your website. This is important when for you too.
You won’t believe what you can find out about your own business.
If I would be doing your website design, I would ask you:
- What industry you are in?
- Who your competitors are?
- Which products or services do you sell?
- What is the price range?
- What are some alternatives to your business offer?
This will identify the starting point of yours or my research. It will provide the basic info that will assure you that you can see what they are doing and where you stand compared to them.
It will also show how you differentiate from them.
Well at least on the basic scale.
And that’s the basics that you need for conducting proper keyword research.
3.4 Plan Out Your Websites Hierarchy
Now, this is where your work starts for real.
In this step, you will basically create a system that will order your data in a logical and user-friendly way.
You design a diagram with the main pages on top and then go from top to bottom to structure your topics.
Make sure it’s simple. This will help you and once you go and start creating your navigation and URL structure.
Something like this.

- As said above, make it logical, as it’s your base for URL structure
- Don’t create too many categories.
- Make sure you are somewhere between 2 and 7. I know that If you are a large business you’ll have more.
- If possible make sure you create a symmetrical structure or close to it. We as human love even things in visuals. But, as you’ll see that’s not possible in every case.
So this is what it looks like in a simple way, but let’s get a bit more concrete.
How to design a website step 4
4. Website Design Content writing
4.1 Determine the Purpose of the Website DESIGN Content
You can’t write good content for a website without knowing why you’re writing it.
Is the website content selling a product? Is it meant to attract new clients? Is it building traffic to support advertising and sponsorships? Once you know the main goal of the website content you’re producing, you’ll be better positioned to write copy that will help achieve that goal.
But before you even write one word of content for a website, know who you’re writing it for.
4.2 Research the Audience
Remember: You’re writing for human readers. People! What you say and how you say it will depend on such things as:
- Their level of expertise. If you expect to be speaking to experts in your website copy, you’re going to use different language than if you’re speaking to novices.
- What they really want to know. This is core to writing effective website content because if you can answer their questions better than anyone else, you have a greater chance of winning them as a customer.
- How they will get to the page. Understanding where your users come from or what they may be searching for when they land on your page can guide how you position your content.
- Their interests. Knowing what your audience is interested in beyond the landing page you’re creating can help you know what elements to add to your website content to keep them engaged on your site.
How do you research your audience?
There are several ways to research your website’s audience. Alexa offers some useful tools for this. For example, Audience Overlap shows you other sites that your visitors are likely to visit. The Audience Interests also shows you topics they are likely to be interested in.
Other ways to research your audience include asking them questions directly, viewing actions they take on your website in your analytics program, and looking for common traits among your best customers.
Researching your competitors will also yield important insights.
4.3 Research Competing Websites
Good website content writing depends on a well-rounded view of the competitive landscape. Comparing your site to your competitors’ yields important insights that will impact the website copy you write. Here’s why:
- Your visitors are visiting your competitors’ websites, too. Learn what they’re reading there, so you can take a stance or offer something different — better — on your website.
- It will help you identify industry trends in website content. You will be able to spot strategic shifts or new tactics competitors are trying early on, rather than being the last to know.
- You can use competitor data to benchmark your performance. Get a sense of the traffic, backlinks, and keywords your competitors’ sites rank for, so you can set realistic goals to measure against each month.
- It can inspire new content topics to write about. You’ll be thankful to have a source of ideas at your fingertips.
This exploratory phase helps you evaluate your options before you write.
How do you research competitors?
Ubersuggest offers some helpful competitive analysis tools. To find a good list of competitors, use the Audience Overlap tool. Once you have that list, analyze competing websites in various ways.
For example, you can find keywords that your competitors are getting traffic for using the Competitor Keyword Matrix. With that information, you can spot how competitive your industry is in terms of SEO. This helps you determine your approach to your website content. Spend some time visiting each of the top competing sites to absorb their style, topics, and how they differ.
One note: At this stage, you’re looking at competing websites as a whole. Later, you’ll also look at individual pages that compete against the web pages you’re writing.
Now that you’ve researched your audience and your competitors’ content, you’ll have an idea of what you want to say.
4.4 Plan How the Content Fits Together on Your Website
Before you step into website content writing, make sure there’s a plan for how all the pages work together.
If you’re overhauling a website or creating a new one, you might find it useful to create a wireframe. This can be as simple as sketching out a list of pages and the topics they’ll cover.
Think through:
- What pages you’ll need and the purpose of each
- How people will navigate to each page
Website content comes in a variety of shapes and sizes. From long-form content and blog posts to sidebar blurbs and product descriptions, copy is prepared and displayed in varied ways to serve different purposes.
4.5 Write the Content for Each Page
Now it’s time to dig into the steps to writing copy for your web pages. Start by understanding the purpose of the page you’re going to write.
Define the Purpose of the Page.
Before you write content for a page on your website, decide what purpose the page will serve. Different pages will have different goals. When thinking through how to write your website content, make sure the copy on each page serves its intended purpose.
For example, your home page serves as a main entrance to your site and helps people understand who you are and what you do at a glance. That means your home page content needs to give people a little bit of information about the most important concepts and help people find where to go next.
You may be writing website content for landing pages, too. Unbounce describes landing pages as pages that have “been designed for a single, focused objective.” They are designed to lead the user to take action and are created for one of the following purposes:
- Click-throughs: a page designed to lead the user to another web page
- Lead generation: a page designed to lead the user to enter their information in an opt-in form
- Purchase: a page designed to lead the user to make a purchase
Some of your pages may be designed to bring in traffic from people who are searching online. If the purpose of your content is to bring in searchers, choose a good keyword to target in your writing.
Find the Best Keyword for the Page.
A keyword is the primary term you want search engines to associate with your page. Before you even start to write, identify the best keyword to target.
How do you find the best keyword?
To identify the best keyword for your page, use Alexa’s Keyword Difficulty tool.
Enter a phrase or term that is related to the topic of your page. Use the filter to limit search results to terms that are low-competition keywords, closely related to your phrase, popular among users, and not a term that is already driving traffic to your site.
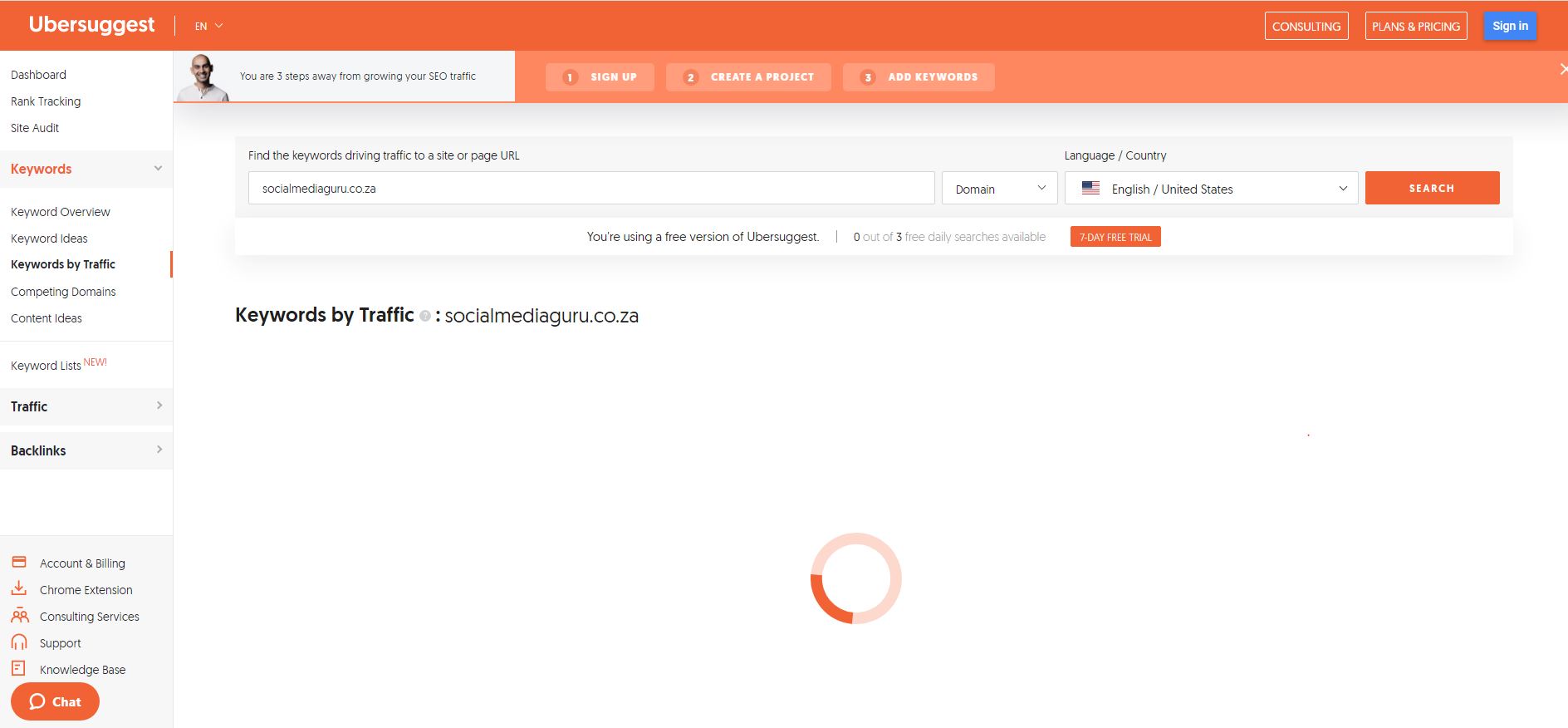
Ubersuggest Keyword Difficulty filters in action for the keyword phrase “content calendar.”
View the report and choose one keyword that is within your competitive reach (indicated by the bolt icon on the report) and widely used by searchers (has a high popularity score). Assign this term to your page as the primary keyword.
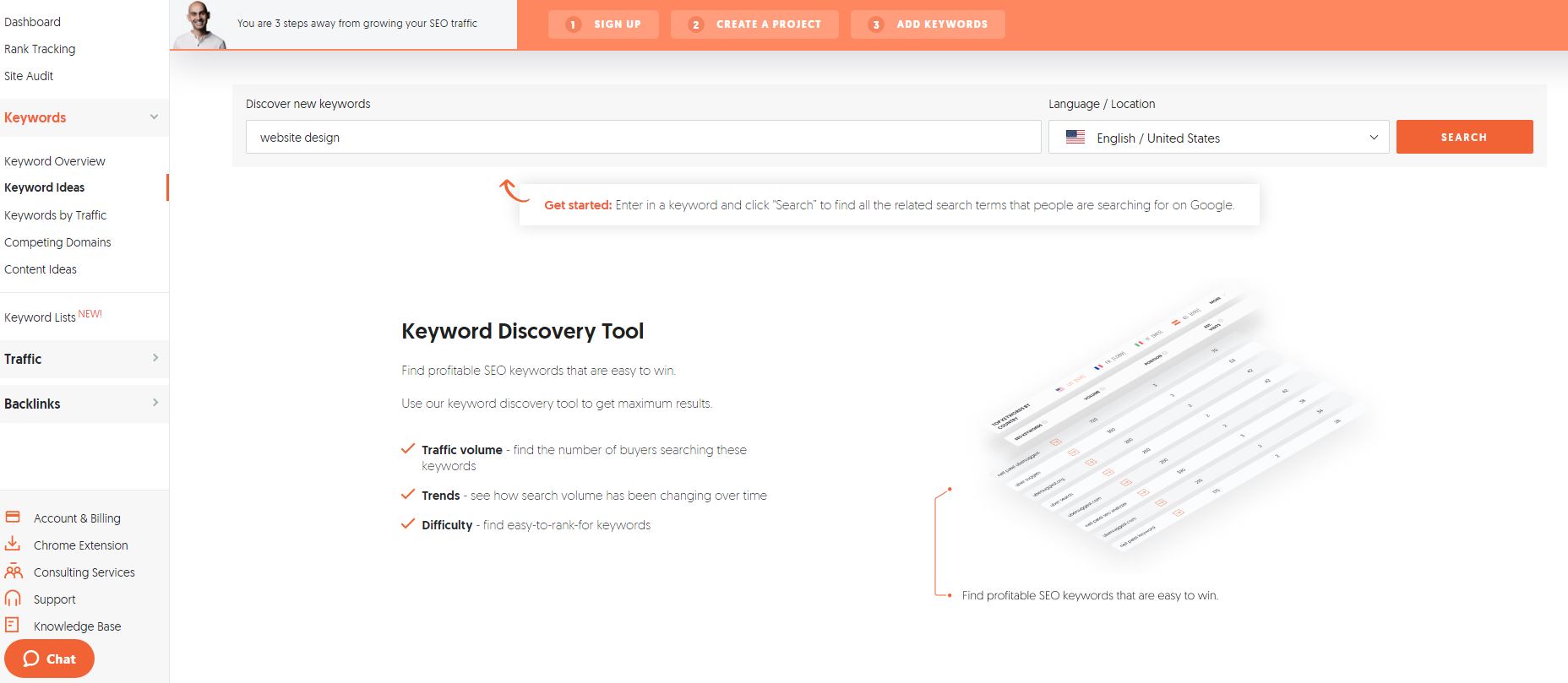
If you want to learn more about selecting keywords, check out The Essential Keyword Optimization Cheat Sheet for Better SEO. Once you go through keyword discovery and select your primary keyword, read on to learn more about how to write content for a website.
Research Popular and Competing Pages.
Which pages will your page compete against? If you know this, you can spot opportunities to create a better page.
One way to do this is to simply enter your target keyword into Google and see which sites are currently showing on page one of the results. Go through them one by one and take note of:
- The length of the page content
- The topics addressed on the pages
- How they format the information (is it in lists or paragraphs?)
Write an Outline and Gather Resources.
To write good content for a website, start with an outline.
Gather ideas and resources, factoring in time for interviews with subject matter experts and sales staff at your organization to help formulate your outline.
Next, create your first draft of the web page copy.
Write the Page Copy.
Dive into writing. As you write content for your website pages, keep these tips in mind.
- Know your goal before you begin. Earlier in this post, we talked about defining the purpose of your page. Keep that purpose in mind as you write. Create all of your content with the intention of driving your audience toward taking the desired action.
- Use the inverted pyramid. This means giving the reader the most important information at the start and less important information toward the bottom. The inverted pyramid style suits how people read on the web.
- Focus on benefits over features. As you highlight products, services, incentives, or offers, show the reader what’s in it for them. Instead of listing features, explain how each feature benefits the reader. For example, don’t talk about a bike’s gear system; talk about the bike’s ability to provide a smooth ride.
- Explain the transformation. Give the reader an idea of how the product, service, incentive, or offer will change their situation. Explain what life is like before and after they take action, and tell the reader how their life will improve once they take the next step.
- Be concise and clear. Use short sentences and phrases. Avoid complex language that loses readers, and cut out any information that is unnecessary or flowery. Stick to saying just what the reader needs to know.
- Avoid buzzwords and jargon. Don’t confuse or lose readers by using high-level terminology they don’t understand. Write using the same language your audience uses when they speak.
- Use bullets and formatting. Help readers find the most important points in your copy by breaking up the text. Highlight main points using bullets, bolding, italics, and variations in font styles and sizes. Most readers scan, so be sure the key points stand out.
- Speak directly to the reader. Copy is more effective when directed right at your audience. Use the same language you would use to speak to your reader in person. Use words like “you” and “your,” and when appropriate, incorporate words like “us” and “we.”
- Stray from grammar rules – if it sounds natural. While you don’t want your copy to include glaring grammatical errors, it’s OK to stray from strict academic writing rules. If it sounds more natural to end a sentence with a preposition or use an incomplete sentence, break the rules. But only break the rules if it adds clarity and a natural sound to the copy. Don’t push the boundaries so much that your copy looks unpolished and sloppy.
Pay special attention to how you wrap up the page.
End the Page With a Strong Call to Action.
As you learn how to write content for a website, you’ll want to consider ways you can encourage the reader to take action from the page. To help initiate that activity, use a clear call to action at the end of every page. Use these tips to tell the reader exactly what you want them to do and why they should take action.
- Include proof. Show readers why they can trust you. Back up your statements by including testimonials, stats, data, and social media mentions that provide proof and support.
- Overcome objections. Put yourself in the shoes of your audience and imagine what objections are holding them back from taking action. Address those concerns and provide options like free trials and money-back guarantees to make it impossible for the audience to resist your offer.
- Use action words. Don’t let your audience be the least bit confused when they reach the end of your page. Include a call to action that uses action words (get started, click here, sign up, call, fill out, etc.) that tells them exactly what they need to do to take the next step.
Now that we’ve addressed the end of the page, it’s time to take another look at the top.
Revisit Your Headline.
You probably wrote a headline for the page when you started working on the copy. By the time you’ve written the whole page, you’ll be ready to revisit it and tweak it to make it more powerful.
Writing headlines for landing pages is slightly different than writing headlines for blog posts and articles. While both are intended to catch attention, headlines for blog posts are designed to make readers interested in a topic, whereas headlines for a landing page are designed to make readers interested in a product, service, incentive, or offer.
Headlines for website content should be:
- Clear: Puns or clever headlines may occasionally work for blog posts or social media, but avoid using them for landing page headlines. Always get right to the point and clearly explain what the page is about.
- Relevant: The headline must be relevant to the content on the page, the call to action, and the link that led the user to the page. Match headlines to the language of the call to action, ad, or promotion that brought the audience to the page. Then ensure that the rest of the copy and call to action are relevant to the main title of the page.
- Desire-focused: Use your headline as an opportunity to introduce the action you’d like users to take when they’ve gotten what they want from your page. In the headline, present the main solution, benefit, or result the action will provide.
Headlines are a great place to focus your effort, as the right headline can make a big difference in how the page performs.
4.6 Add Non-Copy Page Elements
Website content writing guidelines include more than just copy. To create strong, high-converting landing pages and other website content, pay attention to the non-copy elements on the page as well. Insert visuals that show concepts (instead of relying on the words to describe them).
You can break up the page and draw the reader’s eye to important information by using:
- Images
- Buttons
- Text call-outs
- Icons
- White space
- Gifs
- Charts and graphs
- Videos
- Line breaks
- Variations in background colors and images
Putting effort into how you design and write your website content will go a long way toward increasing the chances that your visitors will feel they’ve found all of the information they need.
4.7 Make Edits
Once you’ve written a page’s content, set it aside, even for just a few hours. When you come back to it with fresh eyes, you’ll see ways to improve it.
At this point, you’ll probably find opportunities to:
- Correct typos
- Improve weak word choices
- Rewrite sections that are unclear
- Strengthen the headline
- Link to other content on your site
You may be surprised at what jumps out at you. This is also a good time to optimize your website content for SEO.
4.8 Optimize the Page for SEO
Depending on the purpose of the page, you may want users to find it through search. So as you write content for website pages, use SEO best practices that will help your page rank for your main keyword.
Use the primary keyword naturally throughout the content.
Once you write your content, go back through it and make sure you used your keyword throughout the copy. A keyword density of about 1-2% is ideal, as it is enough to tell search engines what the page is about without stuffing the page with too many uses of the same word, which can negatively affect your ability to rank in search engines.
In addition to using the keyword in the main body copy, also use it in the following SEO content elements:
- Page title (the headline that is visible on the page)
- At least one subheading (the copy that is formatted with H2, H3, H4, etc.)
- Title tag (the 50-60 character page title embedded in the code of the page)
- Meta description (the 150-160 character page summary embedded in the code of the page)
- Image alt tags (the text that describes an image and appears if the image doesn’t load properly)
Link to the new page from other pages on your website.
Help both users and search engines find your new website content by linking to it from other pages on your site. Onsite links help audiences find what they need, and they also send signals to search engines telling them what the page is about and that it has value. Also, when it’s natural to do so, link to landing pages using anchor text that includes the page’s primary keyword.
Double-check the SEO elements on the page.
Even if you optimize your page, it can be easy to miss opportunities or make mistakes. To check on-page SEO and make sure you properly optimize a page, use Alexa’s On-Page SEO Checker. The tool scans your page and provides details on errors and directions on how to resolve mistakes.
Enter your page’s URL and primary keyword into the On-Page SEO Checker.
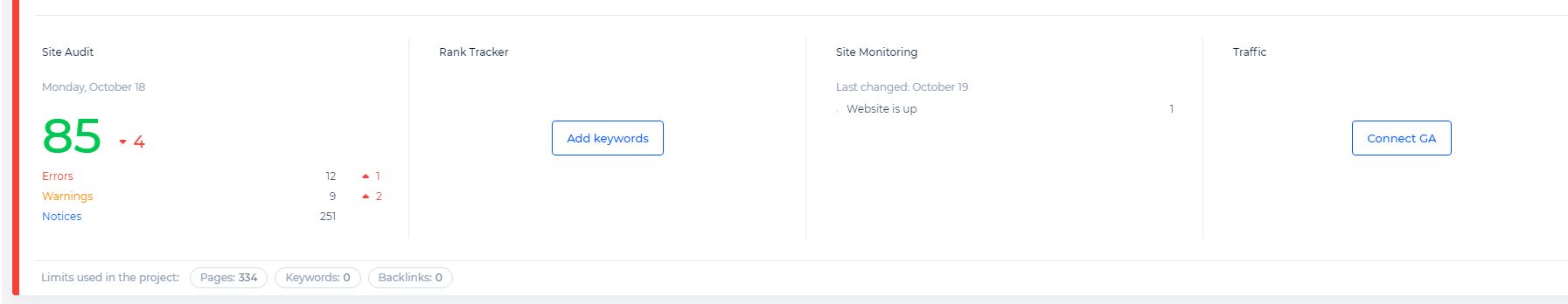
Use the report’s instructions to make changes to your page that will improve your SEO.
4.9 Plan to Update Content Later
If you’re learning how to write content for a website, you might be surprised to hear that your work is really just beginning at this point. It’s important to keep your site content fresh, and now is a great time to plan how you’ll update it later.
Consider A/B Testing Landing Page Content on Your Website.
Especially when writing focused landing pages, you should test different versions of your page to see which creates the most conversions (the percentage of users who complete the desired action on the page).
Create versions of your page with different variations of:
- Headlines
- Subheadings
- Calls to action
- Button colors
- Images
- Layouts
- Features
Then A/B test your pages to see which connects more with users and produces the best results.



